Anticoagulants
(Blood Thinners)
- Why does Atrial Fibrillation cause blood clots?
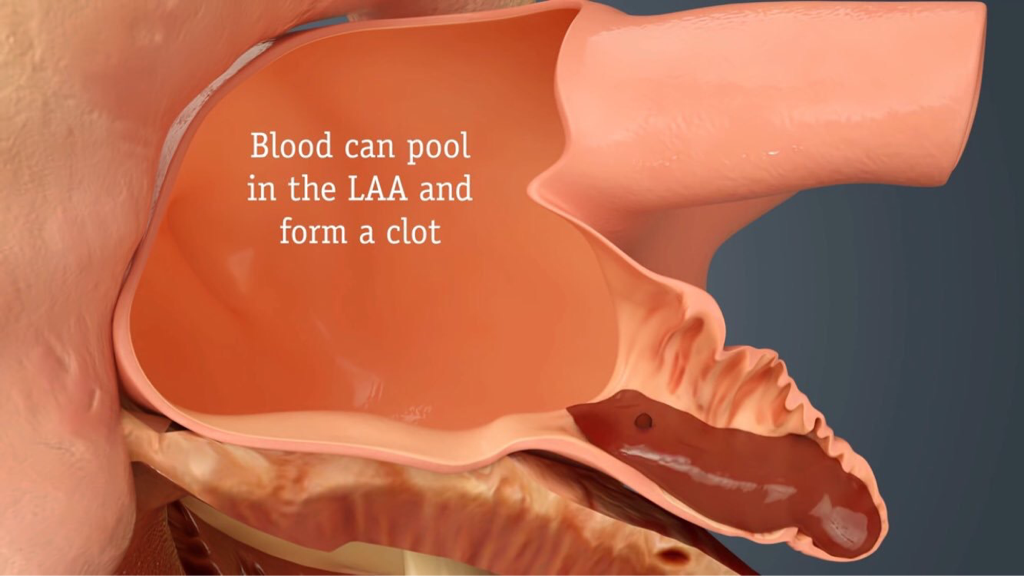
In people with atrial fibrillation, stagnation of blood can lead to blood clots, which can result in blockage to blood vessels in the brain, causing stroke and / or dementia. The blood clots can also interrupt the blood supply to other parts of the body with serious consequences. The risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation can be dramatically reduced by medications which reduce blood clots - these are called anti-coagulant drugs and are often prescribed in patients with atrial fibrillation.
While treatments such as heart rhythm medications, ablation and pacemakers have been shown to reduce symptoms from atrial fibrillation, there is no good evidence that they reduce the risk of blood clots. These treatments should be seen as an addition, not an alternative, to anticoagulants in most people with atrial fibrillation.
- What are the Risks and Benefits of anticoagulants
Factors including age, sex and other medical conditions have a major effect on the risks and benefits of anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation and these should be assessed in making a decision between the patient and healthcare professionals (sometimes this will involve specialist nurses and pharmacists as well as doctors).
- Is Aspirin Effective in Atrial Fibrillation?
- Is Warfarin the best option?
- What about Newer Anticoagulants (NOACS)?
- What does NICE Guidance say?